Reuse an hours module
This tutorial will show you how to add conversational functionality to your chatbot through the reuse of a module.
Background
Modern business applications are typically broken down into a set of services, each responsible for a specific functionality. For example, an airline might have a ticketing service, which includes functionalities such as booking, checking seat availability, and canceling. As interfaces to business functionalities, these services decouple the frontend from the backend implementation of the service, allowing them to be developed independently, making it easier to update and reuse.
Similar to a chatbot, a module is also an OpenCUI frontend project, but it is commonly used to expose a single service conversationally. However, a module does not have the special skill "Main" like a chatbot does, so it cannot be deployed to serve users on its own. Modules are like libraries, they need to be imported into an application like a chatbot to be effective.
Backend implementations of a service are typically deployed separately. A provider is designed to offer a convenient way for the frontend to interact with a remote service implementation as if it were a local function, while handling the necessary network communication details behind the scenes. For a provider to be usable, it needs to be configured so that it has the correct endpoints and required credentials. Once configured, it can be used by every chatbot in the organization. The following diagram shows how chatbots, modules, and providers typically work together:
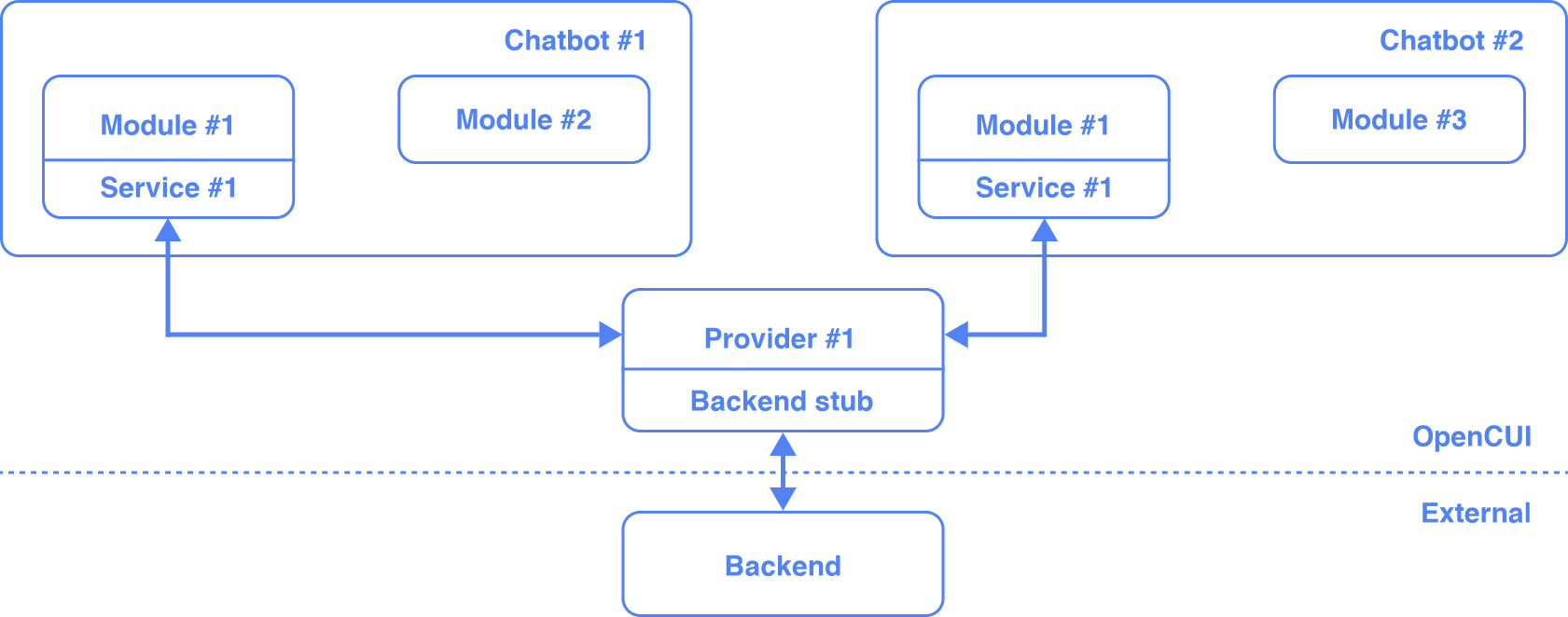
A module of a service paired with a compatible provider is all you need to provide this service conversationally. These pre-built, often higher quality modules are a cost-effective way for you to introduce conversational functionalities to your chatbot. Here are the steps involved:
- Decide on a service you want to expose. Make sure the module and provider are of high quality.
- Set up a compatible provider into your organization and configure it. You can do this by cloning the provider.
- Import the module of that service into the chatbot of your choice.
- Wire the provider to the service in the chatbot configuration.
Before you start
- Log in to OpenCUI.
- We assume that you have finished clone a simple chatbot.
- We assume that you have finished build a simple chatbot.
Pick a module
OpenCUI is designed to promote reusability of both frontend and provider. When you want to add some functionalities to your chatbot, pick a module that meets your needs. Make sure the module of choice has a compatible provider, preferably OpenCUI hosted one like PostgreSQL provider so that you can try them with the least effort. Reusing a module allows you to quickly increase the scope of the service that you offer conversationally, without incurring the high costs and long lead times associated with developing from scratch.
This guide will show you how to reuse an existing module along with a compatible provider, to field users' questions about your business hours.
Here is an example that illustrates how this chatbot can helps users get business hours:
User: "Hello, what time do you open?"
Chatbot: "Our business hours in a week are
Mon 10:00 AM – 11:00 PM
Tue Closed
Wed 10:00 AM – 11:00 PM
Thu 10:00 AM – 11:00 PM
Fri 10:00 AM – 11:00 PM
Sat 10:00 AM – 11:00 PM
Sun Closed"This chatbot can also show the business hours for a particular day, in addition to the business hours for the week. For example:
User: "Hi, are you open this Friday?"
Chatbot: "We are open on Friday, March 31, 2023 from 10:00 AM to 11:00 PM."Set up a provider
To allow a module to interact with a backend service implementation that is already deployed, you need to set up a compatible provider in your organization and configure it so that it can connect to the actual backend.
Instead of building a backend and setting up a provider from scratch, in this guide, you will clone a PostgreSQL provider. The PostgreSQL provider is hosted by OpenCUI, which means that the corresponding backend implementation is also built and managed by OpenCUI. This backend is essentially a relational database with service APIs implemented in SQL and made available in RESTful. Additionally, this backend comes with an admin interface called "backoffice," which allows business operators to populate the database with their business data.
PostgreSQL provider contains not only a stub that abstracts the complexities of communication to masquerade remote services as local functions, but also the schema needed to create the database, as well as SQL function definitions that can be turned into stored procedures. This allows OpenCUI to build and deploy a fully functional backend for a PostgreSQL provider upon request. The PostgreSQL provider is automatically configured and has no external dependencies, making it a very convenient way to provide full-stack conversational functionalities for small and medium-sized businesses.
The backend for other provider is assumed to be deployed as a completely separate concern. But for the PostgreSQL provider to work, you need to make sure the corresponding backend is deployed first. This will trigger OpenCUI to create a managed PostgreSQL instance for your organization and deploy the backend based on that. This includes but is not limited to the following tasks:
- Creating the tables for hosting data for the first time, or altering table structure based on changed annotations.
- Deleting all composite types and creating them again for use as function parameters or returns.
- Making these tables available for both the back office and chatbot through RESTful APIs.
Once the backend is deployed, you need to populate it with your business data. For this use case, you set the business hours for each day of the week, as well as the hours for special occasions.
Clone provider: Hours
To clone the Hours provider, inside hoursProvider, click Clone and set its Project label to hoursProvider (it is ok to set to something else, but let's use this label in the quickstart).
Deploy PostgreSQL backend
To deploy PostgreSQL backend, click Deploy backend button in the upper-right corner of the Versions area.
Populate database
Before the backend can serve relevant information, you need to populate the database with your business hours. You can do this using the backoffice. For every organization that uses at least one PostgreSQL provider, OpenCUI also creates a web application for that organization to manage the data in the backend. You can access the back office as follows:
- Inside the provider
hoursProvider, select the Settings tab, click Configuration on the left sidebar. - Copy and paste the URL to your browser, use Admin email and Admin password to log into backoffice.
In the PostgreSQL backoffice, tables are grouped into namespaces on the left sidebar. The namespace is identified by a provider label, and the table is referenced by a frame type label.
Set up business hours
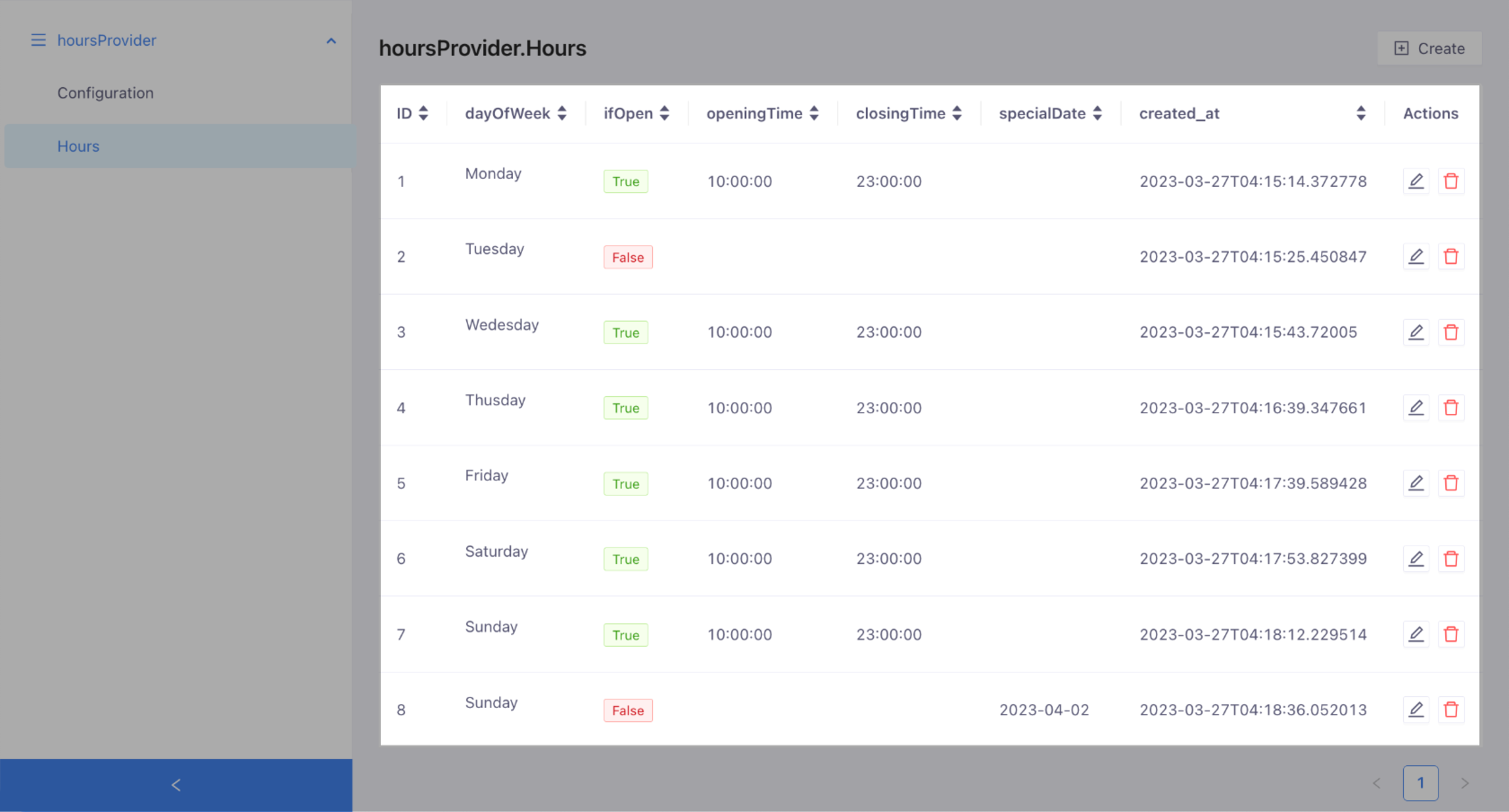
Each business has different hours and unique special days. This provider uses a table called 'Hours' to keep a record of this business-specific hours information. Before serving actual user queries, you need to populate this table with your hours.
To set business hours for each day of the week and for special days, follow these steps:
Inside the
hoursProviderdatabase, click Create on theHourstable.
Fill in the following information in the form and click Save:
- dayOfWeek (Required): The day of the week to add business hours.
- ifOpen (Required): Select True if you are open on that day, or False if you are closed.
- openingTime (Required if
ifOpenisTrue): The time when you open on that day. - closingTime (Required if
ifOpenisTrue): The time when you close on that day. - specialDate (Optional): If you have special days, such as holidays, on which you do not hold regular hours, you can set them up using this column.
Need to know
Currently, only one set of business hours can be set per day as the service is only designed for simple use cases.
Reuse module in chatbot
On OpenCUI, importing modules is another way to reuse conversational functionalities. Unlike cloning a project where you use existing work as a starting point and modify anything to fit your needs, but you cannot benefit from any improvements that will be introduced to the source project after you clone it. With an imported module, it has to fit your needs from the get-go, as there are only limited things, mostly at the language layer, that you can customize. On the other hand, you can always upgrade an imported module to a newer version with bugs fixed and improved experiences.
Reusing the conversational functionality in a module is simple: just import the module with the desired functionality into your chatbot and connect the service to a configured provider in your organization.
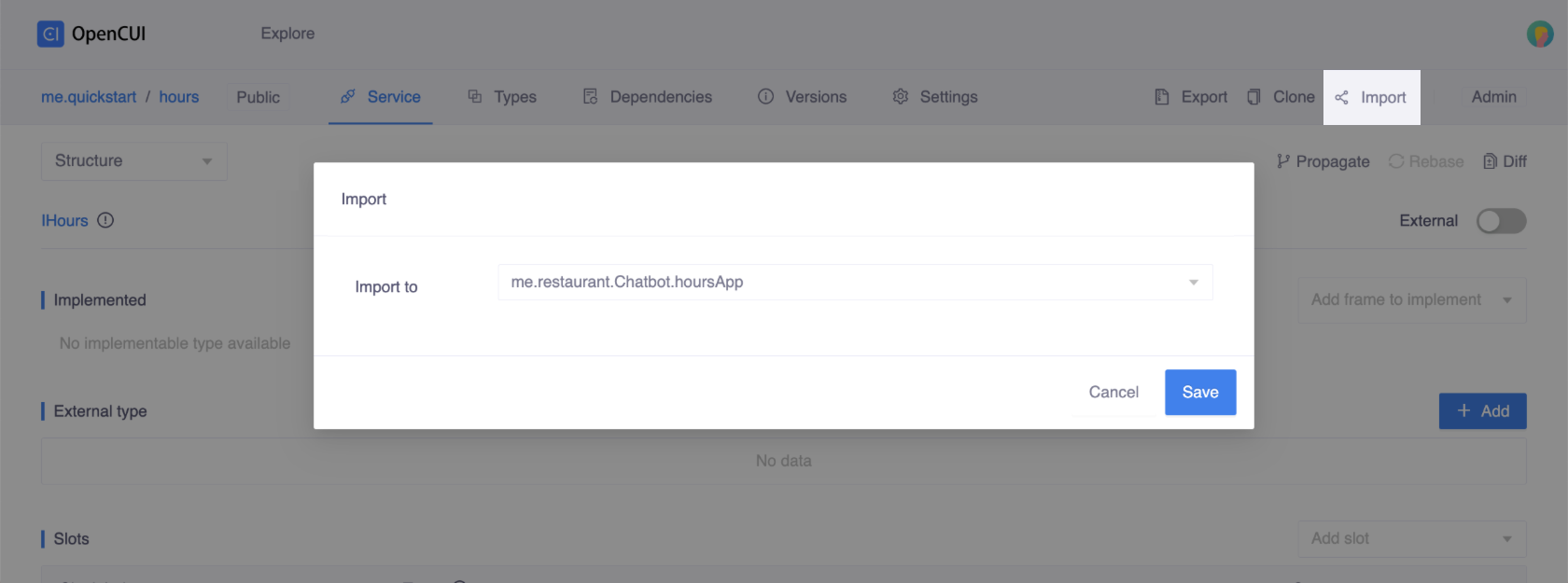
Import the module
To import the module that meets your needs into a chatbot, follow these steps:
- In the hours module, click Import in the top-right corner of the page.
- Select the chatbot you want to import into and Save. If you don't have a chatbot yet, you need to create or clone one before importing.
Wire the provider
For each service that is referenced in the chatbot, you need to wire a provider to it so that the chatbot, or the module imported into the chatbot, can actually access the service implementation. You can wire different providers to the same service under different environments.
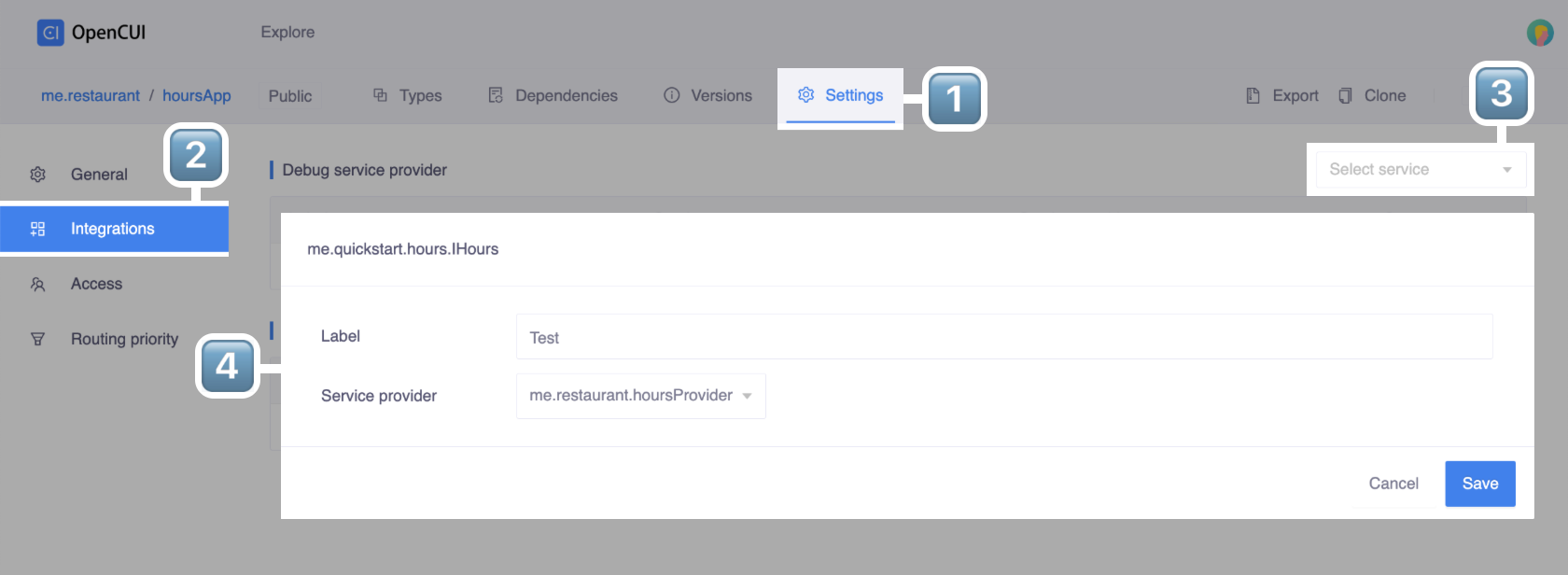
To wire the provider hoursProvider to the module hours service in chatbot's debug environment, follow these steps:
- In chatbot's Settings tab, go to the Integrations page.
- In Debug service provider section, select
me.quickstart.hours.IHoursin the Select service selector. - Fill in the following information in the popup window and Save:
- Enter a unique label such as
Test. This can be used to identify the service in the chatbot's logs. - Select the provider
hoursProviderfor this service. Note that all compatible providers will appear in the drop-down menu.
- Enter a unique label such as
When you are ready to deploy your service to the production environment, you need to repeat the steps above in the Deploy service provider section.
Test a chatbot
Finally, you can try the chatbot for business hours using the built-in Debug tool. To do this, send the following messages to the chatbot:
- "When do you open?" - This will return the business hours for the entire week, starting with the current day of the week.
- "Do you open this Friday?" - This will return the business hours for this Friday, if it is open. If it is closed, you will be informed and the weekly business hours will be shown.
